

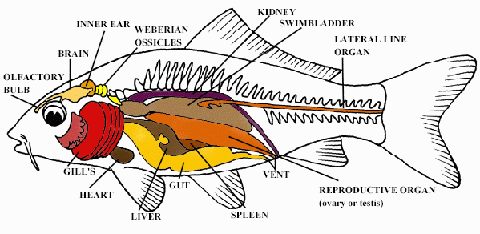
Gills
The gills have three functions. When water is passed over the gills,
oxygen is absorbed and carbon dioxide and ammonium is exhaled. 75% of the
ammonia excreted by the fish is through the gills. The gills also help
the fish osmoregulate, (equalize body pressures). The two gills are located
on the head of the fish, just behind the eyes. They are covered by a boney
flap known as the operculum. Each gill consists of a bone arch with filaments
extending at right angles to the arch. Lamellae are the tiny branches on
the filaments. Healthy gills are bright red and do not stick together.
Signs of trouble with the gills are listlessness, flashing, and rubbing.
Examination of a damaged gill will show excess mucous along with hyperplasia
and a pale color.
Swim Bladder or Air Sac
This glistening oval, dumbbell shaped sac is located in the dorsal
area of the abdomen of the fish, just below the kidney. Its elasticity
allows the fish to have buoyancy and balance. The sphineter muscle opens
to let gases out to the blood stream and the rete mirabile muscle allows
gases in. Futile attempts to swim near the surface or up side down swimming
are signs that the swim bladder is not functioning normally.
Gonads
The sex organs of the fish are termed gonads. In females you will
find the egg sac and in males, the testes. The egg sac may fill a major
portion of the abdominal cavity.
Gastrointestinal Tract
A long, tubular organ; only slightly smaller than the stomach.
The stomach is at the anterior end of the intestine, behind the head and
above the liver.
Spleen
The function of the spleen is to produce and store red blood cells.
It is found embedded in the intestine as a small red mass.
Liver
The liver is responsible for the digestion, filtration and storage
of glucose. It is found in the anterior part of the body cavity as a brownish
red mass. The liver also produces many enzymes that are stored in
the gall bladder. These enzymes assist in the breakdown of food. The liver
functions to store food energy.
Gall Bladder
Digestive enzymes and bile are held here. The gall bladder is a
small sac found embedded in the liver tissue.
Heart
The heart is a two chambered organ. The function of the heart is
to circulate the blood. It is located adjacent to the gills, just behind
the head.
Kidneys
There are two kidneys in a fish. The posterior kidney is located
below the vertebral column and above the air sac. The anterior kidney is
found in front of the air sac. The kidneys produce white blood cells and
filter wastes. Diseased kidneys result in a loss of immunity.
Brain
The brain is located in the head, between but slightly behind the
eyes. It is protected by the skull. The brain controls the voluntary behavior
and involuntary functions of the fish. Erratic swimming or an abscess on
the top of the head could be indications of a problem.
 © Copyright 1996-1998 By
Eduard Freeman
© Copyright 1996-1998 By
Eduard Freeman